GPOPS-II教程(1): 语法和一个最优控制问题案例
一、写在前面
很多同学都在用GPOPS-II做轨迹优化,我在后台里也看见了许许多多的问题来问我。所以想写一个教程,把一些GPOPS-II的例子讲讲,从这些例子中教会如何使用GPOPS-II。
这个教程会分成几个部分,前面几个部分会讲解GPOPS-II的官方案例。通过讲解这些官方案例,说明GPOPS-II的语法应该怎么写,会有什么样的trips。
然后会给出一个总结,总结内容是关于使用GPOPS-II遇见不同问题时,有什么样共性的解决方法,以及各类针对性的解决方法。最后行有余力,给出一个如何调试BUG的教程。
参考文章:
- GPOPS-II教程
- A general-purpose MATLAB software for solving multiple-phase optimal control problems
- A general-purpose MATLAB toolbox for solving optimal control problems using variable-order gaussian quadrature collocation methods
二、GPOPS-II结构
GPOPS-II主要由3部分组成:
- 主函数
main function:用于设置求解问题的各类初始参数,配置GPOPS参数,进行计算并得出结果。 - 连续函数
continuous function:用于表示求解问题的动力学关系,计算每个阶段的被积函数和路径约束。 - 端点函数
endpoint function:用于定义各个阶段初始点和终端点的值,计算求解问题的成本(性能指标)。
在 main function里,要指定求解问题的上下限,以一个阶段(phase)为例,一般包括如下几类:
- 边界条件
bounds- 初始时间、终端时间
- 初始状态、终端状态
- 控制量
- 积分量
- 初值猜测
guess- 初始时间、终端时间
- 初始状态、终端状态
- 控制量
- 积分量
- 路径约束
path - 事件约束
event - 静态参数
auxdata
上述变量,统一被 setup 纳入结构体变量之中。可写作
ouput = gpops2(setup)
其中,其中setup是一个用户定义的结构体变量,该结构体变量包含有关要解决的最优控制问题的所有信息;output是一个结构体变量,其包含通过解决最优控制的问题而获得的信息。下面对setup进行详细解释。
2.1 setup的语法
setup包含必填字段和可选字段。setup中的必填字段如下:
name:不带空格的字符串,对要求解问题的描述;function:包含连续函数continuous function和端点函数endpoint function的结构体;bounds:包含变量和约束的上下限信息的结构体;guess:包含对问题中的时间、状态、控制、积分和静态参数的猜测的结构体。
可选字段如下:
auxdata:辅助数据的结构体,这样就可以不使用全局变量而使用auxdata.args来传递求解问题时所需要用到的部分常量。(args代表任意需要命名的参数,即参数arguments的缩写,无实际意义。)-
derivatives:指定 NLP 求解器所使用的导数近似和 NLP 求解器所使用的导数阶次(first或second)的结构。衍生字段包含derivatives.supplier:NLP 求解器所使用的导数近似,可选值为sparseFD,sparseBD,sparseCD,默认值为sparseFD。derivatives.derivativelevel:NLP 求解器使用的导数阶次,可选值为first,second,默认值为first。derivatives.dependencies:NLP 求解器的依赖关系,可选值为full,sparse,spareseNaN,默认值为sparseNaN。
scales:求解问题时要使用的尺度类型,可选项为none和automatic-bounds,默认值为none。-
mesh:求解问题的网格细化方法,包括网格细化类型、精度公差及初始网格。衍生字段包含mesh.method:网格细化方法,可选值为hp,hp1,默认值为hp1。mesh.options.tolerance:网格要求的精度容差,为0到1之间的正数,默认值为$10$。mesh.options.maxiteration:网格细化最大的迭代次数,为非负整数,默认值为$10^{-3}$。mesh.colpointsmin:网格间隔中配置点最小数量,默认值为$3$。mesh.colpointsmax:网格间隔中配置点最大数量,默认值为$10$。mesh.phase.fraction:每个阶段的网络间隔,是一个0到1的缩放区间,N个间隔,行向量加起来等于1,默认值为0.1*ones(1,10)。mesh.phase.colpoints:每个阶段的配置点,也是行向量,默认值为4*ones(1,10)。
nlp:要使用的 NLP 求解器类型结构体,可选字段包含nlp.solver:求解器类型,可选值为snopt,ipopt。nlp.ipoptoptionsnlp.ipoptoptions.linear_solver:mumpsorma57。nlp.ipoptoptions.tolerance:默认值 $10^{-7}$。nlp.ipoptoptions.maxiterations: 默认值为 $2000$。
nlp.snoptoptionsnlp.snoptoptions.tolerance: 默认值为 $10^{−6}$。nlp.snoptoptions.maxiterations: 默认 $2000$。
2.2 function的语法
指定连续函数和端点函数的函数句柄,代码为
setup.functions.continuous = @continuousfun
setup.functions.endpoint = @endpointfun
2.2.1 setup.functions.continuousfun
格式为
\[\rm function\ output = continuousfun(input)\]输入包括
input.phase(p).time:时间。input.phase(p).state:状态量。input.phase(p).control:控制量。input.phase(p).parameter:静态参数量。
输出是一个长度为 $P$ 的结构向量,包括
output.dynamics:微分状态。output.path:路径约束。output.integrand:积分。
2.2.2 setup.functions.endpoint
格式为
\[\rm function\ output = endpointfun(input)\]输入包括
input.phase(p).initialtime:阶段p的起始时间。input.phase(p).finaltime:阶段p的起始时间。input.phase(p).initialstate:阶段p的起始状态。input.phase(p).finalstate:阶段p的终止状态。input.phase(p).integral:阶段p的积分。input.parameter:阶段p的静态参数。
输出包括两个成员
output.objective:标量,目标函数。output.eventgroup。
2.3 bounds的语法
此处参考GPOPS-II教程。
包括3个成员:
bounds.phase: 指定了时间、状态、控制、路径约束和每个阶段的积分的界限。phase.initialtime.lower: 起始时间的下界。phase.initialtime.upper: 起始时间的上界。phase(p).finaltime.lower: 终止时间的下界。phase(p).finaltime.upper: 终止时间的上界。phase(p).initialstate.lower: 初始状态的下界。phase(p).initialstate.upper: 初始状态的上界。phase(p).state.lower: 每个阶段状态的下界。phase(p).state.upper: 每个阶段状态的上界。phase(p).finalstate.lower: 终止状态的下界。phase(p).finalstate.upper: 终止状态的上界。phase(p).control.lower: 每个阶段控制的下界。phase(p).control.upper: 每个阶段控制的上界。phase(p).path.lower: 每个阶段路径约束的下界。phase(p).path.upper: 每个阶段路径约束的上界。phase(p).integral.lower: 每个阶段积分的下界。phase(p).integral.upper: 每个阶段积分的上界。phase(p).duration.lower: 每个阶段时间的下界。phase(p).duration.upper: 每个阶段时间的上界。
bounds.parameters: 包含问题中静态参数的下界和上界。bounds.eventgroup: 长度为G的结构数组,其中G是问题中事件组的数量。
setup.guess
guess结构体里面的值代表了整个求解过程的初始值
guess.phase(p).time: 阶段p的时间猜测。guess.phase(p).state: 阶段p的状态量猜测。guess.phase(p).control: 阶段p的控制量猜测。guess.phase(p).integral: 阶段p的积分量猜测。
output
gpops2的输出包括
resultresult.solution: 最优的时间、状态和控制以及静态参数。solution.phase(p).time:时间。solution.phase(p).state:状态量。solution.phase(p).control:控制量。solution.parameter:静态参数。
result.objective: 最优值。result.setup:问题设置。result.nextsetup。
meshhistory: 对每个求解NLP的网格进行求解和误差估计。meshiterations: 迭代次数。
上述内容参考自文章GPOPS-II教程,作者kunpeng,遵循CC BY 4.0协议。
三、例题
上面是GPOPS-II的语法部分,了解了GPOPS-II的语法之后,需要例题来帮助理解GPOPS-II的用法。这篇教程里针对一个典型最优控制问题讲解,通过这个理解希望能够让大家明白GPOPS-II中,main function、continuous functioin、endpoint function怎么用。
3.1 问题描述
求解最优控制问题——有约束的停车能耗最优问题
初始时刻车辆位置为$x_1(0)=-2$,速度为$x_2(0)=1$,状态方程为
\[\left\{\begin{matrix} \begin{aligned} \dot x_1(t) &= x_2(t) \\ \dot x_2(t) &= u(t) \end{aligned} \end{matrix}\right. \tag{1}\]容许控制为
\[\left | u \right | \le M_1 =1.5 \tag{2}\]终止条件为
\[x_1(t_f)=0,\ x_2(t_f)=0,\ t_f=2 \tag{3}\]要最小化的性能指标为总能耗,其表达式为
\[J(u)=\int_{t_0}^{t_f}\frac{1}{2}u^2(t)\mathrm dt \tag{4}\]3.2 代码部分
3.2.1 main function
一般会从main function开始写起。
3.2.1.1 初始参数设置
注意到状态初值为$x_1(0)=-2$、$x_2(0)=1$,终止条件里有$t_f=2$,控制约束为$| u | \le M_1 =1.5$。这些都是写代码时首先要加上的初始边界参数,也就是bounds,那么根据式$(2)$、$(3)$和初始条件,给出如下代码:
% 设置时间
t0 = 0;
tf = 2;
% 设置状态量初值
x10 = -2;
x20 = 1;
% 设置控制量边界条件
uMin = -1.5;
uMax = 1.5;
% 设置状态量边界条件
x1Min = -5;
x1Max = 5;
x2Min = -5;
x2Max = 5;
注意,最后4行代码
x1Min = -5;
x1Max = 5;
x2Min = -5;
x2Max = 5;
是按照自己的经验给出的值,不一定非要是这个数值。
3.2.1.2 边界条件设置
下面开始设置边界条件,给出代码如下。
ounds.phase.initialtime.lower = t0;
bounds.phase.initialtime.upper = t0;
bounds.phase.finaltime.lower = tf;
bounds.phase.finaltime.upper = tf;
bounds.phase.initialstate.lower = [x10 x20];
bounds.phase.initialstate.upper = [x10 x20];
bounds.phase.state.lower = [x1Min x2Min];
bounds.phase.state.upper = [x1Max x2Max];
bounds.phase.finalstate.lower = [0 0];
bounds.phase.finalstate.upper = [0 0];
bounds.phase.control.lower = uMin;
bounds.phase.control.upper = uMax;
bounds.phase.integral.lower = 0;
bounds.phase.integral.upper = 10000;
上述代码的意义在上一章全部说明过,这里就不再赘述,只要根据问题的要求就能很自然地写出边界条件。
3.2.1.3 初值猜测
初值猜测的代码如下。
guess.phase.time = [t0; tf];
guess.phase.state = [[x10 x20];[0 0]];
guess.phase.control = [1; uMin];
guess.phase.integral = 100;
写初值猜测的代码时,要注意符号。这里是加的是分号;。
以guess.phase.time = [t0; tf]; 为例,t0是初始时间的猜测值,tf是终端是时间的猜测值,用分号;隔开。其余行的代码同理。
多讲一句,有的同学可能看见第2行代码guess.phase.state = [[x10 x20];[0 0]];很迷糊,因为这里有2个变量。要注意,这个题目里是有2个状态量,$x_1$和$x_2$。所以在写初值猜测guess.phase.state时,也要写成2维变量。[x10 x20]为初始状态的猜测值,[0 0]为终端状态的猜测值。
很多同学问我这里的初值猜测是怎么给出的。
我的回答是只能凭经验给出。
给初值有的时候需要一些运气,给得好,就算得准。
另外,因为该问题只有一个阶段,所以phase为默认值,没有给它设置数值。
3.2.1.4 设置GPOPS-II求解器参数
按照上一章的内容,设置GPOPS-II求解器参数,一般用setup作变量名称。代码如下。
setup.name = 'Vehicle-Stopping-OCP';
setup.functions.continuous = @vsopcContinuous;
setup.functions.endpoint = @vsopcEndpoint;
setup.bounds = bounds;
setup.guess = guess;
setup.nlp.solver = 'snopt';
setup.derivatives.supplier = 'sparseCD';
setup.derivatives.derivativelevel = 'second';
setup.mesh.method = 'hp1';
setup.mesh.tolerance = 1e-6;
setup.mesh.maxiteration = 45;
setup.mesh.colpointsmax = 4;
setup.mesh.colpointsmin = 10;
setup.mesh.phase.fraction = 0.1*ones(1,10);
setup.mesh.phase.colpoints = 4*ones(1,10);
setup.method = 'RPMintegration';
上述代码已在前述章节中讲过,不再赘述。如果同学们在解决自己的问题时,发现求解效果不好的话,可以根据每个变量的选项选择更加合适的选项,优化求解效果。
3.2.1.5 求解
求解代码很简单,代码如下。
output = gpops2(setup);
solution = output.result.solution;
第1行代码是用GPOPS-II进行求解。可不能小看这短短1行代码,它背后的工作是很多很多很多的,GPOPS-II里围绕这个函数做了大量工作,有很多没有显现的函数都是为了GPOPS-II能够正常求解。
第2行代码是获得GPOPS-II求解结果。获得求解结果后,可以开始数据处理了。一般而言,数据处理的方式就是数据可视化(画图)、数据保存、数据分析。
3.2.1.6 画图
这里只给出画图的代码。数据保存和数据分析的代码按需自拟。
figure('Color',[1,1,1]);
plot(solution.phase.time(:,1),solution.phase.state(:,1),'-','LineWidth',1.5);hold on;
plot(solution.phase.time(:,1),solution.phase.state(:,2),'-.','LineWidth',1.5);
plot(solution.phase.time(:,1),solution.phase.control(:,1),'--','LineWidth',1.5);
axis([0 2 -2.5 2]);
xlabel('Time',...
'FontWeight','bold');
ylabel('States',...
'FontWeight','bold');
legend('Pos','Vel','Acc',...
'LineWidth',1,...
'EdgeColor',[1,1,1],...
'Orientation','horizontal',...
'Position',[0.5,0.93,0.40,0.055]);
set(gca,'FontName','Times New Roman',...
'FontSize',15,...
'LineWidth',1.3);
print -dpng Result.png
3.2.2 continuous function
这个部分是问题的动力学方程,防止大家忘记例题的动力学方程是什么样子,在这里再写一遍式$(1)$,公式如下。
\[\left\{\begin{matrix} \begin{aligned} \dot x_1(t) &= x_2(t) \\ \dot x_2(t) &= u(t) \end{aligned} \end{matrix}\right.\]根据动力学方程,写出对应的continuous function,代码如下。
function phaseout = vsopcContinuous(input)
t = input.phase.time;
x2 = input.phase.state(:,2);
u = input.phase.control(:,1);
dx1 = x2;
dx2 = u;
phaseout.dynamics = [dx1, dx2];
phaseout.integrand = 0.5*u.^2;
end
dx1=x2和dx2=u就是动力学方程。
phaseout.integrand = 0.5*u.^2;是性能指标的积分项。同样,再复习一遍该问题的性能指标形式,公式如下。
代码和公式是相互对应的。
3.2.3 endpoint function
这个部分是问题的性能指标函数,即式$(4)$。可以看出,这个问题的性能指标是积分项,所以代码可以像下面这么写:
function output = vsopcEndpoint(input)
J = input.phase.integral;
output.objective = J;
end
3.3 结果分析
根据前述代码,可以得到如下图所示结果。
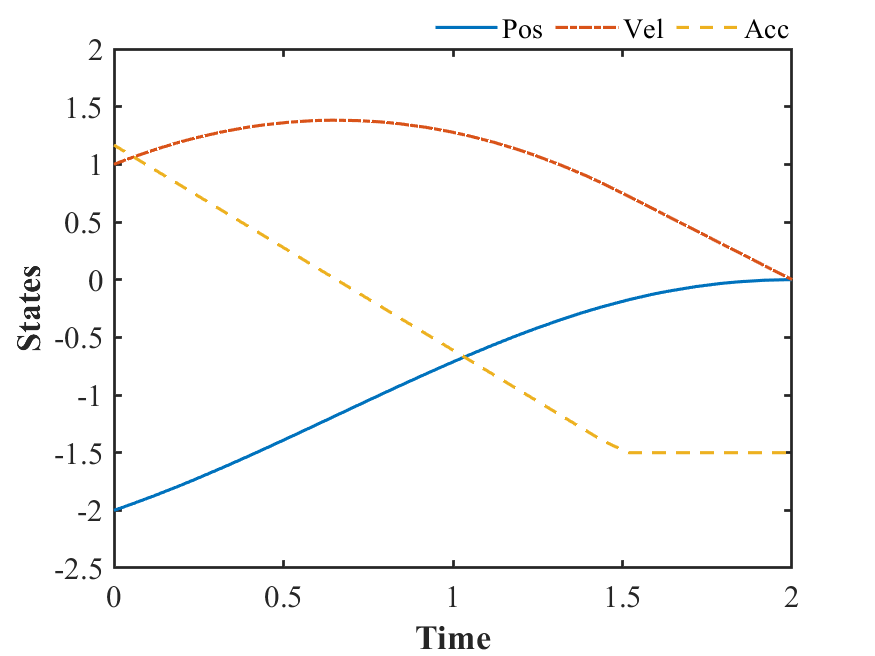
3.4 完整代码
这里给出完整代码。
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
% 功能描述:最优控制问题
% 文件名解释:main_Vehicle_Stopping_OCP.m 中,main 代表 主函数
% Vehcle_Stopping 代表 停车能耗问题
% OCP 代表 最优控制问题.
% 作者:Lei Lie
% 时间:2024/06/21
% 版本:1.0
%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%%
clc;clear;close all;
tic;
%% 01.初始参数设置
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
%----------------------- 设置问题的求解边界 ------------------------------%
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
% 设置时间
t0 = 0;
tf = 2;
% 设置状态量初值
x10 = -2;
x20 = 1;
% 设置状态量边界条件
x1Min = -5;
x1Max = 5;
x2Min = -5;
x2Max = 5;
% 设置控制量边界条件
uMin = -1.5;
uMax = 1.5;
%% 02.边界条件设置
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
%------------------------ 将求解边界设置于问题中 -------------------------%
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
bounds.phase.initialtime.lower = t0;
bounds.phase.initialtime.upper = t0;
bounds.phase.finaltime.lower = tf;
bounds.phase.finaltime.upper = tf;
bounds.phase.initialstate.lower = [x10 x20];
bounds.phase.initialstate.upper = [x10 x20];
bounds.phase.state.lower = [x1Min x2Min];
bounds.phase.state.upper = [x1Max x2Max];
bounds.phase.finalstate.lower = [0 0];
bounds.phase.finalstate.upper = [0 0];
bounds.phase.control.lower = uMin;
bounds.phase.control.upper = uMax;
bounds.phase.integral.lower = 0;
bounds.phase.integral.upper = 10000;
%% 03.初值猜测
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
%------------------------------- 初值猜想 --------------------------------%
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
guess.phase.time = [t0; tf];
guess.phase.state = [[x10 x20];[0 0]];
guess.phase.control = [1; uMin];
guess.phase.integral = 100;
%% 04.设置GPOPS求解器参数
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
%---------------------------- 设置求解器参数 -----------------------------%
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
setup.name = 'Vehicle-Stopping-OCP';
setup.functions.continuous = @vsopcContinuous;
setup.functions.endpoint = @vsopcEndpoint;
setup.bounds = bounds;
setup.guess = guess;
setup.nlp.solver = 'snopt';
setup.derivatives.supplier = 'sparseCD';
setup.derivatives.derivativelevel = 'second';
setup.mesh.method = 'hp1';
setup.mesh.tolerance = 1e-6;
setup.mesh.maxiteration = 45;
setup.mesh.colpointsmax = 4;
setup.mesh.colpointsmin = 10;
setup.mesh.phase.fraction = 0.1*ones(1,10);
setup.mesh.phase.colpoints = 4*ones(1,10);
setup.method = 'RPMintegration';
%% 05.求解
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
%----------------------- 使用 GPOPS2 求解最优控制问题 --------------------%
%-------------------------------------------------------------------------%
output = gpops2(setup);
solution = output.result.solution;
toc;
%% 06.画图
figure('Color',[1,1,1]);
plot(solution.phase.time(:,1),solution.phase.state(:,1),'-','LineWidth',1.5);hold on;
plot(solution.phase.time(:,1),solution.phase.state(:,2),'-.','LineWidth',1.5);
plot(solution.phase.time(:,1),solution.phase.control(:,1),'--','LineWidth',1.5);
axis([0 2 -2.5 2]);
xlabel('Time',...
'FontWeight','bold');
ylabel('States',...
'FontWeight','bold');
legend('Pos','Vel','Acc',...
'LineWidth',1,...
'EdgeColor',[1,1,1],...
'Orientation','horizontal',...
'Position',[0.5,0.93,0.40,0.055]);
set(gca,'FontName','Times New Roman',...
'FontSize',15,...
'LineWidth',1.3);
print -dpng Result.png
%% 函数模块部分
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
% ------------------------- BEGIN: vsopcContinuous.m -------------------- %
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
function phaseout = vsopcContinuous(input)
t = input.phase.time;
x2 = input.phase.state(:,2);
u = input.phase.control(:,1);
dx1 = x2;
dx2 = u;
phaseout.dynamics = [dx1, dx2];
phaseout.integrand = 0.5*u.^2;
end
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
% -------------------------- END: vsopcContinuous.m --------------------- %
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
% -------------------------- BEGIN: vsopcEndpoint.m --------------------- %
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
function output = vsopcEndpoint(input)
J = input.phase.integral;
output.objective = J;
end
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
% --------------------------- END: vsopcEndpoint.m ---------------------- %
% ----------------------------------------------------------------------- %
欢迎通过邮件联系我:lordofdapanji@foxmail.com
来信请注明你的身份,否则恕不回信。